Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, allowing for flexible and cost-effective data storage and computing solutions. The rise of cloud computing has led to an increase in the number of organizations that rely on cloud environments to store and process their data.
However, this reliance on cloud environments also presents a new set of security challenges, as cloud environments are susceptible to a range of vulnerabilities and cyber-attacks.
To ensure that cloud environments are secure, it is important for organizations to implement robust security measures that can assess the security of the cloud environment and identify vulnerabilities. In this article, we will discuss the various security measures that organizations can implement to assess the security of cloud environments and identify vulnerabilities.
Understanding Cloud Security
Cloud security refers to the set of policies, technologies, and procedures that are put in place to protect cloud computing environments from unauthorized access, data theft, and other security breaches. Cloud security is a shared responsibility between cloud service providers (CSPs) and their customers. CSPs are responsible for ensuring the security of the cloud infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing the data and applications that they store and run on the cloud.
There are several security risks associated with cloud computing, including:
Unauthorized access to data
Malware attacks
Denial of service (DoS) attacks
Data breaches
Insider threats
To mitigate these risks, organizations must implement a range of security measures that can assess the security of cloud environments and identify vulnerabilities.
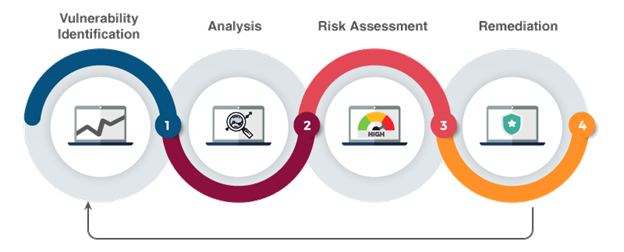
Assessing the Security of Cloud Environments
There are several security measures that organizations can implement to assess the security of cloud environments. These measures include:
Penetration testing
Penetration testing involves simulating a cyber-attack on the cloud environment to identify vulnerabilities and security weaknesses. Penetration testing can be performed by both internal and external security teams.
Vulnerability scanning
Vulnerability scanning involves scanning the cloud environment for potential vulnerabilities and security weaknesses. Vulnerability scanning can be automated or performed manually.
Compliance auditing
Compliance auditing involves assessing the cloud environment against industry-specific compliance standards and regulations to ensure that the cloud environment meets the necessary security requirements.
Risk assessment
Risk assessment involves identifying potential risks and threats to the cloud environment and developing a risk management plan to mitigate these risks.
Identifying Vulnerabilities
Identifying vulnerabilities is an essential step in ensuring the security of cloud environments. There are several techniques that organizations can use to identify vulnerabilities, including:
Network scanning
Network scanning involves scanning the cloud environment for potential security weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Network scanning can be performed manually or using automated tools.
Application scanning
Application scanning involves scanning the applications running on the cloud environment for potential security weaknesses and vulnerabilities. Application scanning can be performed manually or using automated tools.
Code analysis
Code analysis involves analyzing the code used to develop applications running on the cloud environment to identify potential security weaknesses and vulnerabilities.
Mitigating Vulnerabilities
Once vulnerabilities have been identified, organizations must take steps to mitigate them. Mitigation techniques include:
Patching: Patching involves applying security patches to fix vulnerabilities in software and applications running on the cloud environment.
Configuring security settings: Configuring security settings involves ensuring that the cloud environment is configured to meet industry-specific security standards and best practices.
Implementing multi-factor authentication: Multi-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security to the cloud environment by requiring users to provide more than one form of authentication before accessing the cloud environment.
Encryption: Encryption involves encrypting data stored on the cloud environment to ensure that it cannot be accessed by unauthorized users.
Access controls: Access controls involve limiting access to the cloud environment to authorized users only.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, but it has also introduced new security risks and vulnerabilities. To ensure that cloud environments are secure, organizations must implement a range of security measures that can assess the security of the cloud environment and identify vulnerabilities.
These measures include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, compliance auditing, risk assessment, network scanning, application scanning, code analysis, patching, configuring security settings, implementing multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access controls. By implementing these security measures, organizations can ensure that their cloud environments are secure and free from vulnerabilities.