WebSocket is a powerful communication protocol that allows full-duplex, real-time communication between clients and servers. It has gained popularity due to its efficiency, low latency, and ability to facilitate interactive web applications. However, like any technology, WebSocket is not immune to security vulnerabilities. One significant threat is WebSocket hijacking, which allows malicious actors to intercept and manipulate the WebSocket communication between a client and a server. In this article, we will delve into the techniques used by attackers to hijack WebSocket connections and explore countermeasures to protect against such attacks.
Understanding WebSocket
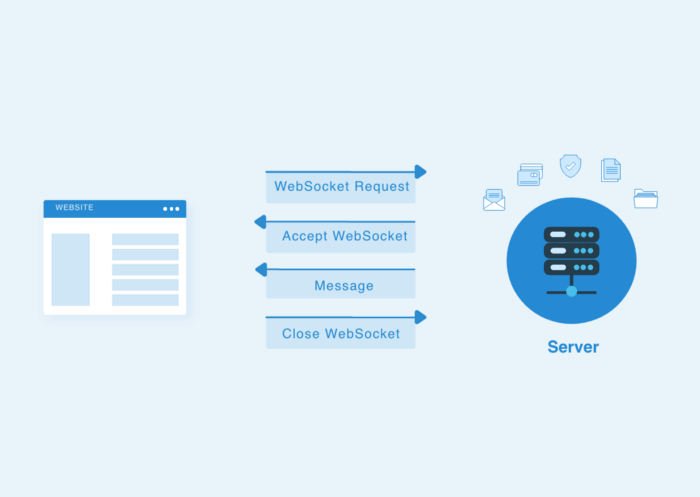
Before we dive into WebSocket hijacking, it's essential to grasp the basics of WebSocket. Unlike traditional HTTP, where the client initiates a request and the server responds, WebSocket provides a full-duplex communication channel, enabling bidirectional data flow. This persistent connection allows real-time updates and eliminates the overhead of establishing new connections for every exchange.
WebSocket starts with an HTTP-based handshake, which upgrades the connection to WebSocket protocol. Once established, data can be sent and received simultaneously by both the client and the server. This feature is especially valuable for applications requiring constant communication, such as chat applications, online gaming, or financial trading platforms.
WebSocket Hijacking Techniques
WebSocket hijacking occurs when an unauthorized third party intercepts and manipulates the WebSocket communication between a client and a server. Attackers can exploit various vulnerabilities to achieve this, some of which include:
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack: In a MitM attack, the attacker secretly intercepts and relays messages between the client and the server. This is typically done using various techniques, such as ARP poisoning, DNS spoofing, or compromised network devices. By gaining access to the data stream, the attacker can eavesdrop, modify, or inject malicious content into the WebSocket communication.
Session Hijacking: If the WebSocket communication relies on an existing session, attackers can attempt to hijack the user's session token or cookie. This could happen due to a vulnerability in the session management process or by exploiting cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the web application.
Cross-Site WebSocket Hijacking (CSWSH): This attack targets web applications with WebSocket endpoints that do not enforce proper cross-origin policies. By leveraging CSRF vulnerabilities, the attacker tricks the victim's browser into making unintended WebSocket connections to the server, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
WebSocket Connection Brute-Force: Attackers may try to brute-force WebSocket connections, attempting various combinations of connection IDs or tokens to gain unauthorized access to an ongoing session.
WebSocket Injection: This technique involves injecting malicious code or data into the WebSocket stream to compromise the client or server-side application. For instance, an attacker could send malicious JavaScript code to the client, leading to XSS attacks.
Countermeasures against WebSocket Hijacking
Mitigating WebSocket hijacking requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both client-side and server-side vulnerabilities. Here are some effective countermeasures to safeguard WebSocket connections:
Secure WebSocket Protocol: When deploying WebSocket, always use the secure version (wss://) instead of the standard (ws://). Secure WebSocket encrypts data during transmission, making it significantly harder for attackers to intercept and interpret sensitive information.
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS): Implement proper CORS policies on the server-side to restrict unauthorized WebSocket connections from other origins. This prevents CSWSH attacks by allowing only trusted origins to communicate with the server.
Authentication and Authorization: Ensure robust authentication and authorization mechanisms are in place. Use strong session management techniques and employ techniques like OAuth tokens to prevent session hijacking.
Encryption and Decryption: Encrypt sensitive data before transmitting it through WebSocket channels. Additionally, implement decryption on the receiver's end to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Input Validation: Implement strict input validation on both the client and server sides to prevent injection attacks. Sanitize and validate user inputs to avoid malicious payloads being injected into the WebSocket stream.
Rate Limiting and Connection Limits: Enforce rate limiting on WebSocket connections to prevent brute-force attacks. Additionally, set connection limits per IP address to avoid resource exhaustion attacks.
Monitoring and Logging: Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging mechanisms to detect suspicious activities or unauthorized access. Regularly review logs to identify potential WebSocket hijacking attempts.
Security Testing and Code Review: Regularly conduct security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, to identify and address potential weaknesses in the WebSocket implementation. Conduct thorough code reviews to spot security flaws early in the development process.
Web Application Firewall (WAF): Deploy a WAF to filter and inspect WebSocket traffic. A well-configured WAF can detect and block malicious WebSocket requests before they reach the application.
Conclusion
WebSocket hijacking is a significant threat to the security of real-time web applications. Attackers can exploit various techniques to intercept and manipulate WebSocket communication, potentially leading to data theft, unauthorized access, or even full application compromise. Implementing robust security measures, such as secure WebSocket protocols, strict authentication, and input validation, as well as regular security testing, can significantly reduce the risk of WebSocket hijacking. By staying vigilant and adopting a proactive security stance, developers and organizations can protect their WebSocket-based applications and ensure a safer online experience for users.