The world of cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking has become increasingly relevant in recent years as governments and organizations around the globe become more reliant on digital technology.
Cyber espionage refers to the practice of using technology to steal sensitive information from governments or organizations, while state-sponsored hacking involves the use of government resources to carry out cyber attacks.
This blog will explore the world of cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking, including the methods used by hackers, the motivations behind these attacks, and the potential impact on individuals, organizations, and governments.
Methods Used by Hackers
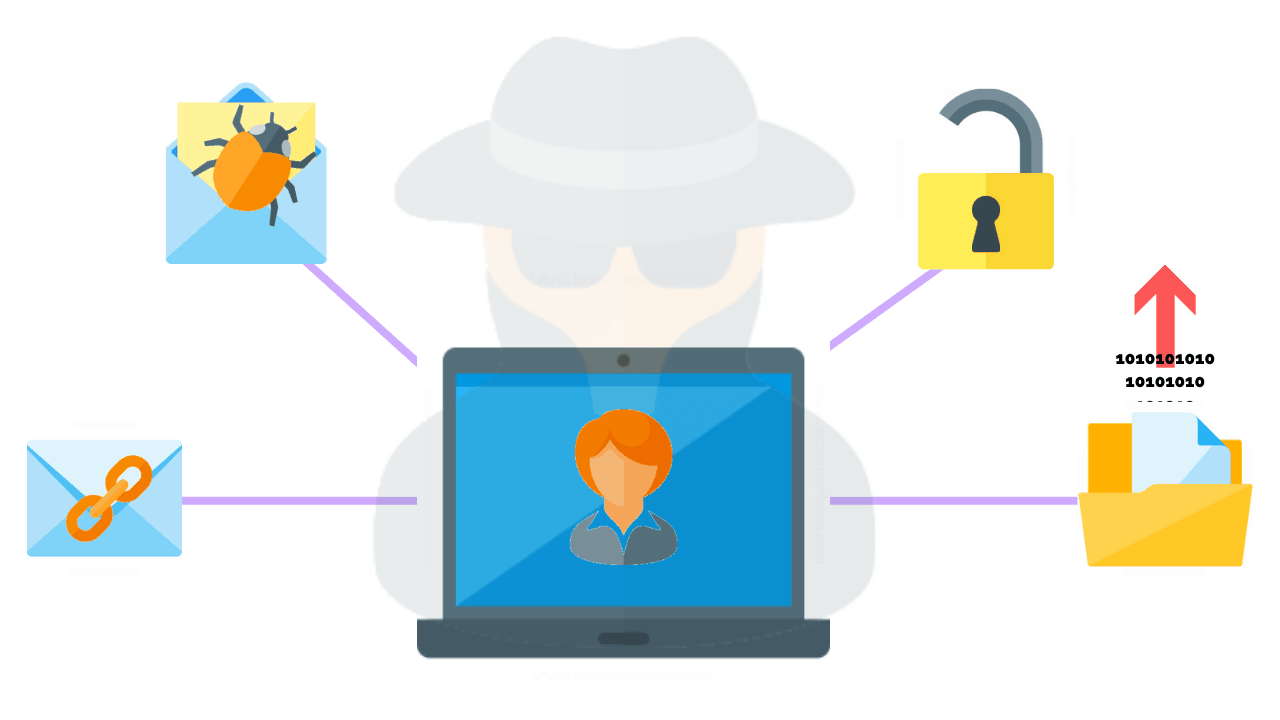
Cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking rely on a variety of methods to gain access to sensitive information or disrupt digital systems. These methods range from simple phishing scams to more sophisticated attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in software or hardware.
Phishing
Phishing scams involve sending deceptive emails or messages that appear to come from a trusted source, but actually contain malicious links or attachments that can infect a system with malware. Malware is a type of software that can damage or compromise a system, allowing hackers to gain unauthorized access or steal sensitive data.
Targeting Vulnerabilities
Another common method used by hackers is the exploitation of vulnerabilities in software or hardware. These vulnerabilities are weaknesses in the code or design of a system that can be exploited by hackers to gain access or take control. Hackers may also use social engineering techniques to gain access to sensitive information, such as tricking employees into revealing passwords or other credentials.
Motivations Behind Cyber Espionage & State-Sponsored Hacking
The motivations behind cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking are varied and complex. In some cases, hackers may be motivated by financial gain, stealing sensitive information such as credit card numbers or personal data that can be sold on the black market.
Other hackers may be motivated by political or ideological reasons, seeking to disrupt or influence the operations of governments or organizations.
State-sponsored hacking is often motivated by geopolitical considerations, such as gathering intelligence or disrupting the operations of rival nations.
Potential Impact of Cyber Espionage & State-Sponsored Hacking
The potential impact of cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking can be significant, both for individuals and organizations.
For individuals, cyber espionage and hacking can result in the theft of personal data, including financial information and sensitive personal details. This can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and other forms of harm.
For organizations, the impact of cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking can be even more significant. Hackers may steal sensitive information such as trade secrets or customer data, which can have a significant impact on the organization's operations and reputation. Additionally, hackers may use malware to disrupt or take control of a system, which can lead to significant downtime and financial loss.
Governments may also be impacted by cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking, as hackers may seek to steal sensitive information or disrupt critical infrastructure. This can have significant implications for national security and may result in the loss of classified information or the compromise of critical systems.
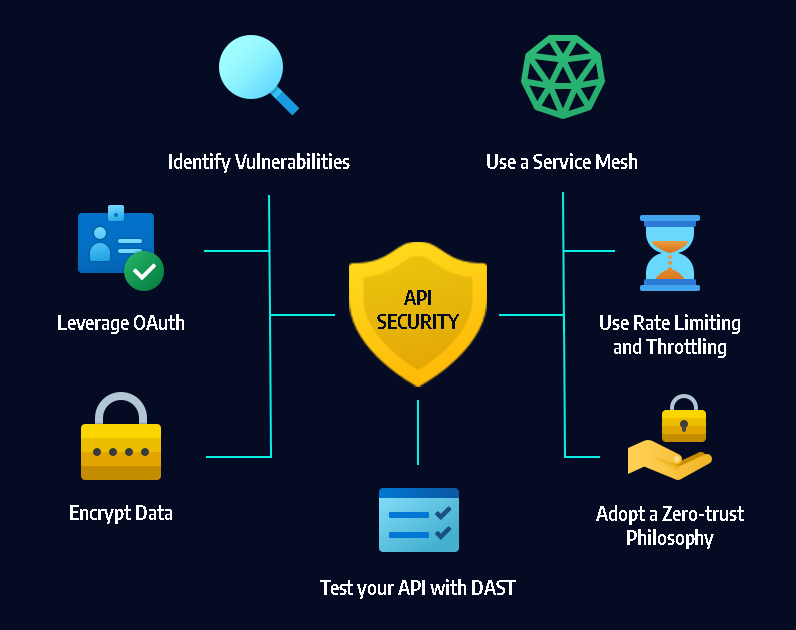
Preventing Cyber Espionage & State-Sponsored Hacking
Preventing cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking requires a multi-faceted approach that involves both technical and non-technical measures. Technical measures include implementing strong security protocols and using up-to-date software and hardware that is resistant to attacks.
Non-technical measures include educating employees about the risks of cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking, and implementing strong policies and procedures for handling sensitive data.
In addition, governments and organizations can work together to share information about cyber threats and collaborate on solutions to prevent and respond to attacks. This includes sharing intelligence about cyber threats, coordinating responses to attacks, and developing international norms and agreements around cyber security.
Conclusion
Cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking represent significant threats to individuals, organizations, and governments around the world. Hackers use a variety of methods to gain access to sensitive information or disrupt critical systems, and their motivations are complex and varied.
Preventing these types of attacks requires a multi-faceted approach that includes technical and non-technical measures, as well as collaboration between governments and organizations.
As technology continues to evolve, the threats posed by cyber espionage and state-sponsored hacking will continue to evolve as well. It is important for individuals, organizations, and governments to remain vigilant and take proactive steps to protect themselves from these threats. This includes staying up-to-date on the latest security measures and best practices, as well as working together to share information and coordinate responses to attacks.