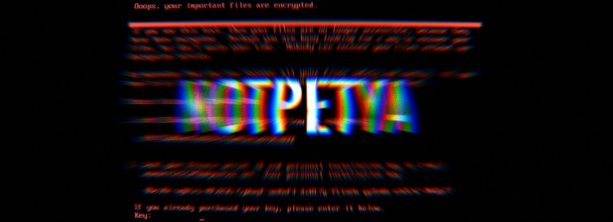
In June 2017, a cyber attack hit companies around the world, causing significant damage and financial losses. The malware responsible for the attack was a type of ransomware known as NotPetya. It is considered one of the most destructive malware attacks in history, causing billions of dollars in damage.
In this article, we will examine the NotPetya ransomware attack and the impact it had on the organizations it targeted. We will also look at the lessons learned from the attack and what steps can be taken to prevent similar attacks in the future.
What is Ransomware?
Before we dive into the NotPetya attack, it's important to understand what ransomware is. Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on a victim's computer, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
Typically, the ransom demand is made in a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, which makes it difficult to trace the attacker.
Ransomware attacks can be devastating for organizations, as they can result in significant data loss, reputational damage, and financial losses. In recent years, we have seen an increase in the number of ransomware attacks, with cybercriminals targeting organizations of all sizes and industries.
The NotPetya Ransomware Attack
The NotPetya ransomware attack was first detected on June 27, 2017. The malware spread rapidly, infecting computers around the world. The initial infection vector for the attack was a malicious software update for a popular Ukrainian accounting software called MEDoc. Once the malware infected a computer, it would attempt to spread to other computers on the same network.
NotPetya was a particularly destructive type of ransomware. Unlike other ransomware attacks that simply encrypt files, NotPetya overwrote the Master Boot Record (MBR) on infected computers. The MBR is a critical component of a computer's operating system that contains information about how the system boots up. By overwriting the MBR, NotPetya rendered infected computers unusable.
Impact of the Attack
The NotPetya attack had a significant impact on the organizations it targeted. In total, the attack is estimated to have caused between $4 billion and $10 billion in damage. Some of the companies that were hit the hardest include:
Maersk - The Danish shipping company was one of the first companies to be hit by the attack. NotPetya caused widespread disruption to Maersk's operations, with some terminals being forced to close. The company estimated that the attack would cost it between $200 million and $300 million in lost revenue.
Merck - The pharmaceutical company was also hit hard by the attack, with the malware causing significant disruption to its manufacturing operations. Merck estimated that the attack would cost it between $275 million and $375 million in lost revenue.
FedEx - The logistics company was forced to shut down some of its operations in Europe after the attack. FedEx estimated that the attack would cost it between $300 million and $400 million in lost revenue.
Lessons Learned
The NotPetya ransomware attack was a wake-up call for many organizations, highlighting the need for better cybersecurity practices. Here are some of the lessons learned from the attack:
Patch Management - The NotPetya attack was able to spread so quickly because it exploited a vulnerability in the MEDoc software. Organizations need to have robust patch management processes in place to ensure that all software is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Network Segmentation - NotPetya was able to spread rapidly through networks because it was able to move laterally from one infected computer to another. Organizations can mitigate this risk by implementing network segmentation, which separates networks into smaller, more secure segments.
Backups - Backups are critical in the event of a ransomware attack, as they allow organizations to restore their data without having to pay a ransom. However, it's important to ensure that backups are stored securely and are regularly tested to ensure that they are working correctly.
Incident Response - Organizations need to have a well-defined incident response plan in place to respond to a ransomware attack quickly and effectively. This includes having a designated incident response team, establishing communication protocols, and regularly testing the plan to ensure that it is effective.
Cyber Insurance - Cyber insurance can help organizations mitigate the financial impact of a ransomware attack. However, it's important to carefully review policy terms and conditions to ensure that the organization has adequate coverage.
Conclusion
The NotPetya ransomware attack was a devastating event that highlighted the destructive potential of malware. The attack caused billions of dollars in damage and disrupted the operations of organizations around the world. However, it also provided valuable lessons that can help organizations improve their cybersecurity practices and better protect themselves from future attacks. By implementing the lessons learned from the NotPetya attack, organizations can improve their cybersecurity posture and reduce their risk of falling victim to a similar attack in the future.